开始
# 开始

# 模板语法
{{ xxx }}:插值表达式(Mustache 语法),xxx为js表达式。
# 渐进式框架
Vue 从设计角度来讲, 虽然能够涵盖这张图上所有的东西,但是你并不需要一上手就把所有东西全用上(主张最少) ,因为没有必要。无论从学习角度,还是实际情况,这都是可选的。声明式渲染和组件系统是Vue的核心库所包含内容,而客户端路由、状态管理、构建工具都有专门解决方案。这些解决方案相互独立,你可以在核心的基础上任意选用其他的部件,不一定要全部整合在一起。
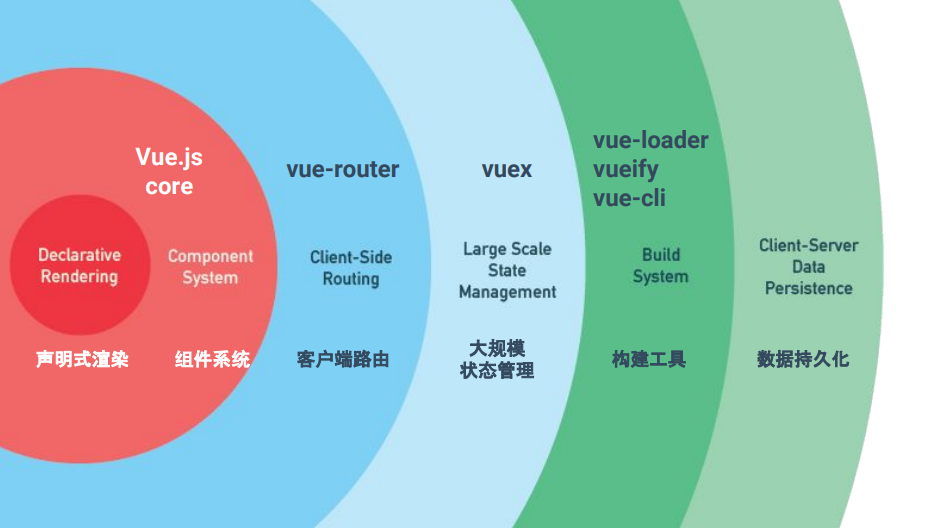
- 声明式渲染:DOM 随状态(数据)更新而更新。(声明式:关注结果,命令式:关注过程(jQuery))
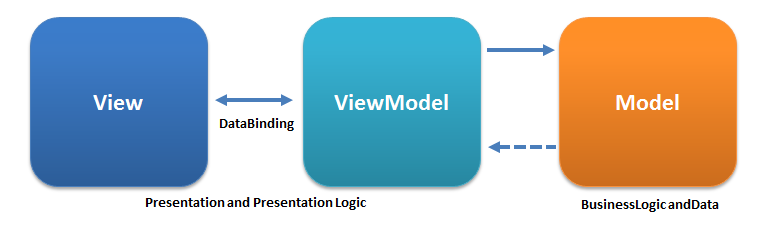
# mvvm 框架
虽然没有完全遵循 MVVM 模型 (opens new window),但是
Vue的设计也受到了它的启发。因此在文档中经常会使用vm(ViewModel的缩写) 这个变量名表示Vue实例。通过用Vue函数创建一个新的**Vue实例**。var vm = new Vue({ // 选项 });1
2
3MVVM(Model–view–viewmodel)是一种软件架构模式 (opens new window),MVVM支持双向绑定,意思就是当 M 层数据进行修改时,VM层会监测到变化,并且通知 V 层进行相应的修改,反之修改 V 层则会通知 M 层数据进行修改,以此也实现了视图与模型层的相互解耦。View 的变动,自动反映在ViewModel,反之亦然。关系图
响应式原理
侵入式:
this.a++(不调用方法)非侵入式:
this.setState({a:this.state.a++})(调用方法)Object.defineProperty() (opens new window)
//基本使用 let obj = { b: 5 }; Object.defineProperty(obj, "a", { // value:5, //设置值 // writable: false, //是否可写(是否能被修改) // enumerable:false,//是否可被枚举(循环对象是否能被输出) get() { console.log("访问a"); return 6; //return的值是设置a的属性,没有return,下次访问a是undifined }, set(newValue) { console.log("设置a"); console.log(newValue); //被设置的值被当做参数传入set }, }); obj.a = 7; console.log(obj.a); //a=6,访问时又走了get,在使用临时变量保存改变的值,在set的时候赋值给临时变量,get中返回临时变量1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17//getter/setter需要临时变量周转才能工作 let obj = {}; let temp; Object.defineProperty(obj, "a", { get() { console.log("访问a"); return temp; }, set(newValue) { console.log("设置a"); temp = newValue; }, }); obj.a = 7; console.log(obj.a);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15//封装成函数defineReactive let obj = {}; function defineReactive(data, key, val) { //data:数据对象,key:键值,val替代临时变量 //函数外部可以访问val的值,get和set闭包中的环境 Object.defineProperty(data, key, { enumerable: true, //可枚举 configurable: true, //可改变或删除 get() { console.log("访问" + key); return val; }, set(newValue) { console.log("设置" + key); if (val == newValue) return; val = newValue; }, }); } defineReactive(obj, "a", 10); obj.a = 4; console.log(obj.a);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22对象代理
function Vue(options) { let _data = options.data() let _this = this Object.keys(_data).forEach(i => {//代理对象添加到实列原型 Object.defineProperty(_this, i, { get() { console.log('Get'+i) return _data[i] }, set(newValue) { _data[i]=newValue return newValue } }) }) } let vm = new Vue({ data() { return { name: 'Blueless Bird', author: 'Joni' } } }) vm.name='Hey Boi.' console.log(vm.name)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27其他
//this.$options.data().xxx获取初始值 //el > $mount //render > template 替换el的内容1
2
3
# 生命周期函数
在某一时刻自动执行的函数(也叫钩子函数)
图谱
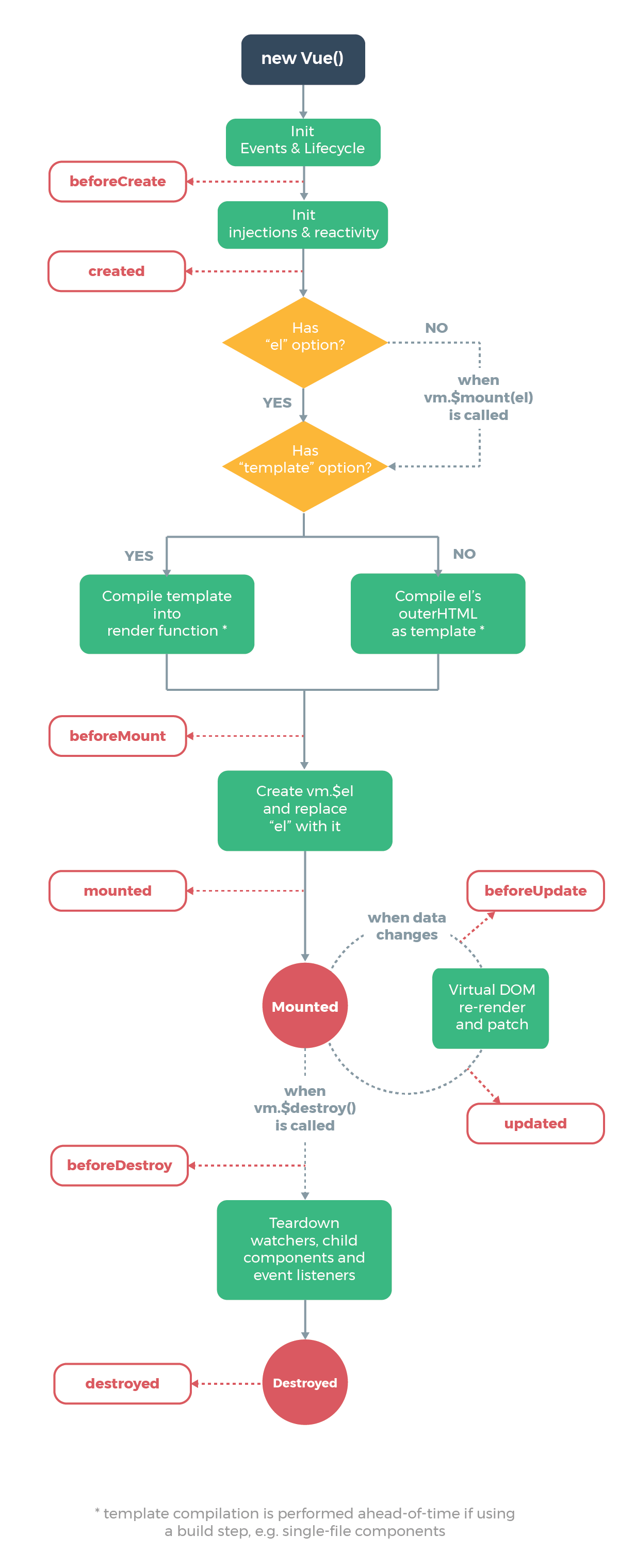
beforeCreate在初始化 / 实例创建 之前执行的函数Created在初始化 / 实例创建 之后执行的函数,可以访问methods, data, computed等上的方法和数据beforeMount在组件内容被渲染到页面之前自动执行的函数
(注意:可获取到
vm.el,但并未挂载)Mounted在组件内容被渲染到页面之后自动执行的函数beforeUpdate在数据将要变化之前自动执行的函数updated在数据发生变化之后自动执行的函数beforeUnmount在VUE实例销毁之前自动执行的函数unmounted在VUE实例销毁之后自动执行的函数errorCaptured捕获一个来自子孙组件的错误时被调用
不要在选项 property 或回调上使用箭头函数 (opens new window),比如 created: () => console.log(this.a) 或 vm.$watch('a', newValue => this.myMethod())。因为箭头函数并没有 this,this会作为变量一直向上级词法作用域查找,直至找到为止,经常导致 Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property of undefined 或 Uncaught TypeError: this.myMethod is not a function 之类的错误。
hook
export default{ methods:{ fn(){ const timer = setInterval(()=>{ //具体执行代码 console.log('1'); },1000); this.$once('hook:beforeDestroy',()=>{ clearInterval(timer); timer = null; }) } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14//父组件 <rl-child @hook:mounted="childMountedHandle" /> //vue3 改为@vnode-updated method () { childMountedHandle() { // do something... } },1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9父子组件生命周期执行顺序
初始化:
原理:子组件作为父组件的DOM子节点,父组件实例化完成后要挂载这个父组件,调用父组件的render方法方向有子组件,则去 创建渲染子组件并缓存(因为可能有多层),子组件都完成完成父组件的挂载 子组件挂载完成后,父组件还未挂载
更新 同理:先完成子组件的更新,再完成父组件
父beforeUpdate -> 子beforeUpdate -> 子updated -> 父updated
销毁
父beforeDestroy -> 子beforeDestroy -> 子destroyed -> 父destroyed
# 计算属性
计算属性:依赖 data 中的数据进行计算,与 methods 不同的是只有响应式依赖发生改变时才进行重新计算(计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的)。模板内的表达式非常便利,但是设计它们的初衷是用于简单运算的。在模板中放入太多的逻辑会让模板过重且难以维护。
2复制代码计算属性的 getter 和 setter
当我们取计算属性值的时候会执行 get 方法(模板使用),设置的时候会执行 set 方法,computed 属性默认为 getter,但是它还提供了 setter,可以由因变量去影响自变量。
wangcai
复制代码
# 侦听器
监听属性,属性变化时,自动执行里面的函数,参数:
current(现在参数的值),prev(以前参数的值)<input v-model="firstName" type="text" /> <p>{{fullname}}</p> <script> export default { watch: { firstName: function (n, o) { //改变firstName,执行函数,改变fullname this.fullname = n + this.lastName; console.log(o); }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13深度监听
handler方法和immediate属性最初绑定的时候是不会执行的,要等到
firstName改变时才执行监听计算,修改一下 watch 写法使其初绑定的时候就执行。watch: { firstName: { handler(n, o) { this.fullname =n+this.lastName console.log(o) }, immediate:true }, },1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9deep属性watch里面还有一个属性deep,默认值是false,代表是否深度监听。<input v-model="obj.a" type="text" /> <p>{{ obj.a }}</p> <script> export default { data(){ return { obj: { a: 123 }, } } watch: { obj: { handler() { this.obj.a = 567; console.log("change"); }, //immediate: true, deep: true //obj.a变化时执行函数,给对象的所有属性都加上监听器 }, }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22//优化,使用字符串形式监听 watch: { 'obj.a': { //只给obj.a加监听器 handler() { console.log("change"); }, immediate: true, deep: true }, },1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
注销 watch
watch 写在组件中,会随着组件的销毁而销毁。如果使用下面这样的方式写 watch,那么就要手动注销。
const unWatch = app.$watch("text", (newVal, oldVal) => { console.log(`${newVal} : ${oldVal}`); }); //返回unWatch方法 unWatch(); // 手动注销watch1
2
3
4
5watch 监听路由
可以使用 watch 来进行路由的监听
watch: { changeShowType(value) { console.log("-----"+value); }, '$route'(to,from){ console.log(to); //to表示去往的界面 console.log(from); //from表示来自于哪个界面 if(to.path=="/shop/detail"){ console.log("商品详情"); } } },1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 过滤器
用于一些常见的文本格式化,用在双花括号插值和 v-bind 表达式中。
# 指令
v-text
与花括号的区别是在页面加载时不显示{{}}。
在的前后可以添加其他的内容,而在 v-text 里面不行。
v-html更新元素的
innerHTML复制代码注意
- 在网站上动态渲染任意 HTML 是非常危险的,因为容易导致 XSS 攻击 (opens new window)。只在可信内容上使用
v-html,永不用在用户提交的内容上。 - 在单文件组件 (opens new window)里,
scoped的样式不会应用在v-html内部,因为那部分 HTML 没有被 Vue 的模板编译器处理。如果你希望针对v-html的内容设置带作用域的 CSS,你可以替换为 CSS Modules (opens new window) 或用一个额外的全局<style>元素手动设置类似 BEM 的作用域策略。 - 浅谈XSS攻击的那些事 (opens new window)
- 在网站上动态渲染任意 HTML 是非常危险的,因为容易导致 XSS 攻击 (opens new window)。只在可信内容上使用
v-show
根据变量控制 dom 显示与隐藏,变量为 false 时,display:none,
v-show不支持<template>元素,也不支持v-else。v-if
根据变量控制 dom 显示与隐藏,变量为 false 时,直接移除 dom 元素。
v-if与v-for一起使用时,v-for具有比v-if更高的优先级。v-bind
缩写:
:绑定 html 标签中的属性值。<a :[type]="'http://www.baidu.com'">百度</a> <!--写静态要在""中加''--> <br /> <a :[type]="url">百度</a> <script> export default { data() { return { type: "href", }; }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13v-on
缩写:
@事件监听器,- 事件修饰符:
@click.prevent(阻止默认行为) - 模板中绑定事件:
<Son @click=‘handleClick’> \</Son> $event传递原生事件:hanclick(count,$event),不传参数,第一个参数为e
- 事件修饰符:
# 修饰符
表单:lazy,trim,number事件:stop(冒泡),prevent(阻止默认),capture(捕获,使事件触发从包含这个元素的顶层开始往下触发),once(只触发一次),self(只当在 event.target 是当前元素自身时触发处理函数),passive(onscroll事件加一个.lazy),native(监听根元素的原生事件)鼠标、键盘:left、right、middle:鼠标左、右、中键点击,keycode:对应键盘码
# 样式绑定
字符绑定:在 data()在定义变量,v-bind 绑定属性
给时光以生命,给岁月以文明复制代码对象绑定:传给
:class一个对象给时光以生命,而不是给生命以时光复制代码或者
<div :class="{ red:false,green:true}">{{message}}</div>1数组绑定:把数组传给
:class<div :class="['red', 'active']">{{ message }}</div>1或者 data()中定义数组
或许是不知梦的缘故,流离之人追逐幻影。复制代码行内动态样式
字符串形式
The closer you look,the less you see.复制代码对象形式
These violent delights have violent ends复制代码
其他
复制代码复制代码
# 列表循环
v-for:循环可迭代对象(数组,对象,字符串,数字),
vue要求增加 key 值**(字符串、数值)**避免重复渲染。- 零化域的缺失之环
- 闭时曲线的碑文
- 对偶福音的规约
- 模糊像散的孤独
- 二律背反的双重人格
- 永劫回归的潘多拉
- 回折叙唱的鹅妈妈
- 盟誓的文艺复兴
复制代码index 作为 key,逆序添加、逆序删除会导致key发生变化当成新的节点,产生没有必要的真实 DOM 更新
数组方法:
1. push():从数组尾部添加内容
2. unshift():从数组头部添加内容
3. pop():从数组末尾删除内容
4. shift():从数组头部删除内容
5. sort():对数组进行排序
6. reverse():对数组进行取反
7. splice():从数组中筛出具体的内容
循环与判断不写在同一标签上,
v-for的优先级比v-if更高。
# 虚拟DOM
JS按照DOM结构来实现的树形结构对象
graph LR A(数据改变)-->B(虚拟dom计算变更)-->C(真实dom)-->D(视图更新)1
2//snabbdom import {init, classModule,propsModule, styleModule,eventListenersModule, h} from "snabbdom"; //使用snabbdom库 const patch = init([classModule, propsModule, styleModule, eventListenersModule]); //初始化patch函数 const vNode = h("ol", {}, [ //标签,属性,孩子节点/文本节点(children和text只会存在一个) h("li", null, "one"), h("li", null, "two"), ]);//h函数创建vNode并返回 const container = document.getElementById("container");//容器 patch(container, vNode); //将vnode替换空容器,如果patch第一个参数为真实dom,创建vnode并关联dom const newVnode = h("ol", null, [ h("li", null, "one"), h("li", null, "two"), h("li", null, "three"), ]); patch(vNode, newVnode)//更新dom,vNode已关联dom1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16diff
同级比较:Diff算法比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
patch:对比当前同层的虚拟节点是否为同一种类型的标签,是继续执行patch进行深层比对,不是把节点替换成新虚拟节点
sameVnode:判断是否为同一类型节点(key值,标签名。。。)
# 双向绑定
v-modle:本质上是语法糖text和textarea元素使用valueproperty 和input事件;checkbox和radio使用checkedproperty 和change事件;- select 字段将
value作为 prop 并将change作为事件
记忆就像镜子,映照出灵魂的模样。
复制代码An act of creation always begins with an act of destruction.
复制代码修饰符
v-model.lazy失去焦点才触发双向绑定v-model.number用户输入的值自动转变为 number 类型v-model.trim去掉字符串前后空格.sync修饰符类似于
v-modle,也是一个语法糖,使子组件能够修改父组件的值,不限制标签<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> .sync的使用 <el-button v-if="!show" @click="show=true">显示</el-button> <Son :visible.sync="show" /> <!--:visible.sync="show"是 @update:visible="(val)=>{show = val}" 和 :visible="show"的语法糖--> </div> <script> import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; export default { name: "App", data() { return { show: false, }; }, components: { Son, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23<!--子组件--> <div v-if="visible"> 对话框 <el-button @click="$emit('update:visible', false);">隐藏</el-button> <!--触发update:visible事件改变父组件的值--> </div> <script> export default { name: "Son", data(){ return { }, props: { visible: { type: Boolean, default: false }, }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 组件
组件注册(定义==>注册==>使用)
定义子组件(子组件必须要有唯一的根标记)
<div>我是子组件</div> <script> export default { name: "Son", data(){ return {//一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数,如果 Vue 没有这条规则,就会影响到其它所有实例 } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9注册组件
//根组件中全局注册 /*Vue.component('my-component-name', { // ... 选项 ... })*/ import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; import Vue from "vue"; Vue.component("Son", Son); //组件命名 大驼峰引入,大驼峰或横线注册,html中大驼峰或横线使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!--父组件中局部注册并使用--> <div> 我是父组件 <Son /> <Son /> </div> <script> import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; import Son1 from "./components/Son1.vue"; export default { components: { Son, //"Son":Son简写,为了和普通变量区分,建议首字母大写 Son1, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
父子组件通信
# 父子组件的关系可以总结为
prop向下传递,事件向上传递。父组件通过自定义属性传值,子组件
props接收.camelCase(驼峰命名法) 的prop名需要使用其等价的 kebab-case (短横线分隔命名) 命名不能修改传递过来的数据
<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> 我是父组件 <Son :message="msg" /> <!--使用v-bind绑定动态Prop--> <Son :message="msg1" /> </div> <script> import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; export default { name: "App", data() { return { msg: "hello!", msg1: "Son", }; }, components: { Son, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<!--子组件--> <div>{{ message }}</div> <script> export default { name: "Son", data(){ return { }, props: ['message'],//以字符串数组形式列出的 prop,prop不能与data中的数据重名 } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11Prop验证:props为带有验证需求的对象,prop验证失败的时候,Vue将会产生一个控制台的警告props: { // 基础的类型检查 (`null` 和 `undefined` 会通过任何类型验证) propA: Number, // 多个可能的类型 propB: [String, Number], // 必填的字符串 propC: { type: String, required: true }, // 带有默认值的数字 propD: { type: Number, default: 100 }, // 带有默认值的对象 propE: { type: Object, // 对象或数组默认值必须从一个工厂函数获取 default: function () { return { message: 'hello' } } }, // 自定义验证函数 propF: { validator: function (value) { // 这个值必须匹配下列字符串中的一个 return ['success', 'warning', 'danger'].indexOf(value) !== -1 } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31子组件触发自定义事件传值
<!--子组件--> <button @click="increment">子组件(点击传值)</button> <script> export default { name: "Son", //如果向父组件传递的方法很多,可以在这里标识出来 //emits 可以是数组或对象,从组件触发自定义事件,emits 可以是简单的数组,也可以是对象,后者允许配置事件验证。 emits: ['increment'], methods: { increment(){ this.$emit('increment',2,'第二个参数')//触发自定义事件传值, }, } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> {{count}} <!--自定义事件,通过$emit触发--> <Son @increment="add" /> </div> <script> import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; export default { name: "App", components: { Son }, data() { return { count: 0, }; }, methods: { add(value, sec) { //触发事件时传的值 this.count += value; console.log(value); console.log(sec); }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26父组件传方法,子组件调用
<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> {{count}} <Son :change="add" /> <!--传递了add方法,父组件的方法能改变父组件的数据--> </div> <script> import Son from "./components/Son.vue"; export default { name: "App", components: { Son }, data() { return { count: 0, }; }, methods: { add(value) { //子组件调用时传值 this.count += value; console.log(value); }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25ref 属性
<!--子组件--> <div>子组件</div> <script> export default { name: "Son", data(){ return { message:'子组件数据', }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> {{msg}} <Son ref="son" />//绑定ref </div> <script> import Son from './components/Son.vue' export default { name: 'App', components: {Son} mounted(){ this.msg=this.$refs.son.message console.log(this.$refs.son.message) //通过$refs获取组件实例,得到组件数据和方法 }, data(){ return{ msg:'', } }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23slot 插槽
父组件控制插槽是否显示、怎样显示,子组件控制槽在哪显示(占位符)
slot写在组件template的什么位置,父组件传过来的模板将来就显示在什么位置。<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> 父组件 <Son @change="add">插槽内容:{{msg}}</Son> <!--标签内容显示在子组件的<solt>元素位置,插槽内可以包含其他html标签或其它的组件,作用域为父组件作用域,没有<solt>元素则废弃标签内容--> </div> <script> import Son from './components/Son.vue' export default { name: 'App', components: {Son} data(){ return{ msg:'父组件数据', } }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<!--子组件--> <div>子组件</div> <slot>默认内容</slot> <!--父组件什么都不写的话显示默认内容--> <!--一个不带name的<slot>出口会带有隐含的名字“default”--> <!--任何没有被包裹在带有 v-slot 的 组件标签 中的内容都会被视为默认插槽的内容--> <!--v-slot只能添加在<template>上或自定义组件上(只有一种例外情况)-->1
2
3
4
5
6
7具名插槽:
< slot name=”mySlot”>有命名时,组件标签中使用属性slot=”mySlot”的元素就会替换该对应位置内容<!--父组件--> <Son> <div slot="header">头部</div> <!--标签内部什么都不写显示默认内容--> <div slot="content">内容</div> <!--新写法`#`为`v-slot:`的缩写--> <div #footer>页脚</div> </Son>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!--子组件--> <slot name="header">默认内容</slot> <slot name="content">默认内容1</slot> <slot name="footer">默认内容2</slot>1
2
3
4作用域插槽:子传父传参的方式,解决了普通
slot在 parent 中无法访问 child 数据的问题父级模板里的所有内容都是在父级作用域中编译的;子模板里的所有内容都是在子作用域中编译的。
<!--子组件--> <h1>子组件</h1> <slot :data="list" name="son">{{def}}</slot> <!--子组件把list传递给插槽,不写name,name为fefault--> <script> export default { name: "Son", data(){ return { def:'默认内容', list: [ "起源与终结的序章","时空跳跃的妄想症", "并列过程的偏执狂","空理彷徨的会谈", "电荷冲突的接点","蝶翼的偏差值", "断层的变动率","梦幻的自平衡", "时空境界的信条","自我相似的雌性同株", "形而上的坏死","虚像歪曲的混合", "因果律的溶解","镜面上的命运石之门" ], }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<!--父组件--> <Son> <template #son="prop"> <!--父组件使用一个变量来接收,这里变量为prop(随便取名),也可以解构{list},prop作为参数传入函数--> <li v-for="(v,i) in prop.list" :key="i">{{v}}</li> </template> </Son>1
2
3
4
5
6
7https://juejin.cn/post/6954284127528943629
http://www.jianboge.com/d148386
# 动态组件 & 异步组件
动态组件:通过动态属性
is结合component标签实现,<component /:is="xxxx" />,通常和keep-alive一起使用保持组件状态,is的值为组件名、组件对象或函数式组件。Component1Component2Component1Component1复制代码复制代码异步组件:异步执行某些组件逻辑,加载页面时会下载所有组件代码,异步组件类似路由懒加载(按需加载),优化性能。
<!--基本使用--> <div id="app"> 异步组件的使用 <button @click="show=!show">{{show?'隐藏':'显示'}}</button> <Son v-if="show" /> </div> <script> import Son from './components/Son.vue' export default { name: 'App', components: { Son:()=>(import(/*webpackChunkName:'Son'*/'./components/Son.vue')), //当show为true时才加载js代码并缓存代码,webpackChunkName可以给该js文件取名 } data(){ return{ show: false, } }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22<!--异步组件工厂函数--> <div id="app"> 异步组件的使用 <button @click="show=!show">{{show?'隐藏':'显示'}}</button> <AsyncComponent v-if="show" /> </div> <script> import Error from './components/Error.vue' import Loading from './components/Loading.vue' import Son from './components/Son.vue' //异步组件工厂函数 const AsyncComponent=()=>({ component:import (/*webpackChunkName:'Son'*/'./components/Son.vue'),//promise对象 loading:Loading, error:Error, delay:200,//延迟200ms(先显示loading组件) timeout:3000//超过3000ms显示error组件 }) export default { name: 'App', components: { AsyncComponent } data(){ return{ show: false, } }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31vue3 使用辅助函数
defineAsyncComponent声明,component选项更名为loader,选项可以添加onErorr回调重试动态异步组件
//组件对象 const loading = { name: "loading",//keep-alive排除组件 template: '<div >加载中....</div>', }; const error = { name: "error", template: '<div >加载错误</div>', inject: ["reload"], created() { this.reload && this.reload(); //重试 }, }; const component = { template: '<div >I am async!</div>', };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<keep-alive :exclude="['error', 'loading']"> <!-- keep-alive需要排除error,loading组件--> <component :is="AsyncComponent" ></component> </keep-alive> <script> export default { data() { return { attempts: 0, isGetCom: false, } }, computed: { AsyncComponent(){ return () => ({ component: new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(component); }, 1500); }), error, loading, delay: 0, timeout: 1000, }) } }, } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31异步组件失败解决
<!--method1:利用key刷新父组件--> <async-com :key="attempts" /> <script> //vm.$forceUpdate()可以迫使 Vue 实例重新渲染。注意它仅仅影响实例本身和插入插槽内容的子组件,而不是所有子组件。 //重要提示:这不会更新任何计算属性,调用`forceUpdate`仅仅强制重新渲染视图。 import AsyncCom from "./components/AsyncCom.vue"; export default { data() {return { attempts: 0, //key放动态组件上会因为timeou时间已过导致无限循环 }; }, provide: function () { return { reload: this.reload, //error组件中调用 }; }, methods: { reload() { if (this.attempts < 10) console.log("尝试次数", ++this.attempts); }, }, components: { AsyncCom, }, </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<!--method2:更新计算属性的依赖项更新计算属性,导致视图更新--> <script> export default { data() {return { attempts: 0, }}, computed: { AsyncComponent() { return () => ({ component, error,loading, delay: 0,timeout: 1000, attempts: this.attempts, }) } }, methods: { reload() { if (this.attempts < 10) { //与方法1类似error组件调用 console.log("尝试次数", ++this.attempts); } }, } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<!--method3:获取组件后更新计算属性--> <script> let component//使用变量保存组件 export default { data() { return { isGetCom: false,//改变依赖触发计算属性更新 } }, computed: { AsyncComponent() { if (!this.isGetCom) return () => ({ component: new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(() => { const com={ template:'<div>I am async!</div>', }; component=com this.isGetCom=true//计算属性重新计算 //resolve(this.component); }, 1500); }), error, loading, delay: 0, timeout: 1000, }); else return component; }, }} </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# Mixin 混入
提取组件公共逻辑(包含任意组件选项如 data,mehoods,生命周期)
//定义minin export default { data() { return { dataCommomd: "公共数据", }; }, methods: { methodsCommomd() { console.log(this.type + "公共方法"); }, }, mounted() { console.log("公共mounted"); }, };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16<!--子组件A(组件B类似)--> <template> <div> <button @click="methodsA"> 组件A方法 </button> <button @click="methodsCommomd"> 公共方法 </button> </div> </template> <script> import mixin from './mixin' export default { mixins:[mixin], data(){ return{ aData:'组件A的数据', type:"组件A" } }, methods: { methodsA(){ console.log("组件A的方法") } }, mounted(){ console.log('组件A的mounted') console.log(this.type+this.dataCommomd) } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32<!--父组件--> <div id="app"> <h1>Minin的使用</h1> <component-a /> <hr /> <component-b /> </div> <script> import componentA from "./components/ComponentA.vue"; import componentB from "./components/ComponentB.vue"; export default { name: "App", components: { "component-a": componentA, "component-b": componentB, }, data() { return {}; }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21优先级
- 数据和方法:组件 data ,methods 优先级高于 mixin data,methods 优先级
- 生命周期:生命周期函数,先执行 mixin 里面的,再执行组件里的
- 自定义的属性,组件中的属性优先级高于 mixin 属性的优先级
其他
- 局部
Mixin:mixins:[myMixin],myMixin是一个自定义组件 - 全局
Mixin:app.mixin( ) Vue3中尽量避免使用Mixin,因为可以使用CompositionAPI来代替,可维护性更高。
- 局部
# extends
# 依赖注入
祖先组件使用provide选项向后代提供数据/方法,后代组件通过inject 选项接收property,property是非响应式的。
<!--祖先组件-->
<Son />
<script>
import Son from "./components/Son";
const store = Vue.observable({ name: "张三" });
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "Some people choose to see the ugliness in this world.The disarray.I choose to see the beauty",
obj:{name:'dax1'},//同样是响应的
};
},
provide: function () {//对象或返回一个对象的函数
this.store = store;
return {
store: this.store,//如果你传入了一个可监听的对象,那么其对象的 property 还是可响应的
msg: this.msg,
parent: this, //当前组件实例
};
},
mounted() {
this.store.name = "李四";
},
components: {
Son,
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
<!--后代组件-->
<div>{{this.msg}}</div>
<script>
export default {
inject: ["msg", "parent"],//一个字符串数组,或一个对象
mounted() {
console.log(this.parent);
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 事件总线
vue2
//定义eventbus //event-bus.js import Vue from "vue"; export const eventBus = new Vue(); //eventBus就是一个Vue实例1
2
3
4<!--组件1--> {{ age }} <el-button @click="add">加1</el-button> <script> import { eventBus } from "./event-bus.js"; //需要是同一个eventBus export default { data() { return { age: 18, }; }, methods: { add() { this.age++; eventBus.$emit("add-age"); //发送消息 }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<!--组件2--> {{ age }} <el-button @click="add">加1</el-button> <script> import { eventBus } from "./event-bus.js"; export default { data() { return { age: 18 } }, methods: { add() { this.age++; }, }, created() { eventBus.$on("add-age", () => { this.age++; }); //接收消息 }, beforeDestroy() { // 如果没有提供参数,则移除所有的事件监听器; // 如果只提供了事件,则移除该事件所有的监听器; // 如果同时提供了事件与回调,则只移除这个回调的监听器。 eventBus.$off("add-age", () => { this.age++; }); }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29vue3
//使用mitt import mitt from 'mitt' app.config.globalProperties.$bus = mitt();1
2
3<!--组件1触发--> <script lang="ts" setup> import { getCurrentInstance } from "vue"; const { proxy } = getCurrentInstance(); function emit() { proxy.$bus.emit('message',{msg:'北海虽赊,扶摇可接'}) } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!--组件2监听--> <script lang="ts" > created() { this.$bus.on('search',(e:Object)=>{ console.log(e); }) }, </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# directive
定义方法
全局:
app.directive('focus',{mounted(el){el.focus()}})局部:局部指令需要在父组件注册后才可以使用
directives: { focus: { // 指令的定义 inserted: function (el) { el.focus() } } }
//navActive.js export default { //指令就是对象 bind: (el, bind) => { // console.log('bind') // console.log(el) el为指令绑定的dom元素 // console.log(bind); bind.value可以拿到绑定指令传的值 el.onclick = () => { //点击更改样式变红,获取父元素把重置兄弟元素样式 el.className = "el-button el-button--danger"; const children = Array.from(el.parentNode.children); children.forEach((v, i) => { if (i !== bind.value.index) v.className = "el-button el-button--default"; }); }; }, };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18<div> <!--3个按钮,指令传index,bing.value获取--> <el-button v-nav-active="{index:i}" v-for="(v,i) in 3" :key="i" >按钮{{v}}</el-button > </div> <script> import NavActive from "./navActive.js"; export default { name: "Son", directives: { NavActive, //注册指令 }, data() { return {}; }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18生命周期函数
# 渲染函数
字符串模板之外的另一种选择,允许你充分利用 JavaScript 的编程功能。
<!-- 不加:会解析为string类型 -->
<Son :leave=1>黄金色的树林里分出两条路,</Son>
<Son :leave=2>可惜我们不能同时去涉足,</Son>
<Son :leave=3>但我们却选择了,</Son>
<Son :leave=4>人迹罕至的那一条,</Son>
<Son :leave=5>这从此决定了</Son>
<Son :leave=6>我们的一生。</Son>
2
3
4
5
6
7
<p :style="`font-size:${fontSize}`"><slot/></p>
<script>
export default {
name: "Son",
props: ["leave"],
computed: {
fontSize: function () {
if (this.leave % 2) {
return 10 + (6 - this.leave) * 3 + "px";
} else {
return 10 + (6 - this.leave) * 2 + "px";
}
},
},
};
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
使用render函数创建标签
黄金色的树林里分出两条路,
可惜我们不能同时去涉足,
但我们却选择了,
人迹罕至的那一条,
这从此决定了
我们的一生。
- 岁月流转,念念不忘,群碑未成,来日方长
- 日斜映影渐薄,犹待来者,重托衣钵
- 她实惠君良多,更有无穷,待君探索
- 此路或有蹉跎,君莫忘,必有灵犀相佐
# Vue-Router路由
安装:Vue add router
根据 URL 的不同,展示不同的内容
//route/index.js文件 import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; import layout from "../components/Layout.vue"; import Son from "../components/Son.vue"; import notFond from "../components/NotFond.vue"; Vue.use(Router); //使用插件 //该插件实现1.声明并全局注册router-link与router-view2.实现install:this.$router.push() export default new Router({ //创建实例 mode: "history", //路由模式,默认hash,history无# base: process.env.BASE_URL, //配置路由表(路由规则) routes: [ { path: "/", name: "home", component: layout, }, { path: "son", name: "son", component: Son, }, { path: "*", name: "notFond", component: notFond, }, ], }); //匹配到path路径后找对应的component组件,在'router-view'处渲染 //匹配不到路径渲染notFond组件1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33//还需要在main.js中将路由实例挂载给Vue实例 import router from "./router/index.js"; new Vue({ router, render: (h) => h(App) }).$mount("#app"); //添加配置项1
2
3<!--app.vue一级路由匹配到的组件将显示在路由出口--> <template> <router-view></router-view> </template>1
2
3
4动态路由
路由传参,通过 route.param 接收
//路由index.js import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; const routes = [ { path: "/", name: "home", component: layout, children: [ { path: "/login", name: "login", component: Login, }, { path: "/reg", name: "reg", component: Reg, }, //动态路由,参数名为id { path: "/user/:id", name: "user", component: User, }, ], }, { path: "*", name: "notFond", component: notFond, }, ]; Vue.use(Router); export default new Router({ mode: "history", base: process.env.BASE_URL, routes, }); //解决重复点击报错 const originalPush = Router.prototype.push; Router.prototype.push = function push(location) { return originalPush.call(this, location).catch((err) => err); };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44<!--user组件--> <template> <div>用户信息{{id}}</div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { id: this.$route.params.id, //直接这么写页面上的id并不会变化,路由变化并不会重新创建组件,id是初始化的时候赋值的所以不会改变 }; }, watch: { //监听路由或使用组件内路由守卫改变id $route(n, o) { this.id = n.params.id; console.log(o); }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21嵌套路由
//重新定义路由表 routes: [ { path: "/", name: "home", component: layout, children: [ { path: "/login", name: "login", component: Login, }, { path: "/reg", name: "reg", component: Reg, }, ], }, { path: "*", name: "notFond", component: notFond, }, ],1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25<el-container> <el-aside width="200px">Aside</el-aside> <el-container> <el-header>Header</el-header> <el-main >Main <!--点击跳转路由切换router-view内容--> <router-link to="/login">登录</router-link> <router-link to="reg">注册</router-link> <!--二级路由将显示在这--> <router-view></router-view> </el-main> <el-footer>Footer</el-footer> </el-container> </el-container> <!--配合element的Container布局容器-->1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16动态添加路由
<el-container> <el-aside width="200px">Aside</el-aside> <el-container> <el-header>Header</el-header> <el-main >Main <a @click="login">登录</a> <router-link to="/reg">注册</router-link> <router-link to="/new" v-if="isLogin">动态添加的路由</router-link> <router-view></router-view> </el-main> <el-footer>Footer</el-footer> </el-container> </el-container> <script> import New from "./New"; //新路由 const newRouter = [ { path: "/new", component: New, }, ]; export default { data() { return { isLogin: false, }; }, methods: { login() { this.isLogin = true; this.$router.push("/login"); this.$router.addRoutes(newRouter); }, }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37addRoutes添加的路由为一级路由,,如果是二级路,那要把父路由、祖先路由也带上,否则不会识别。vue3改用router.addRoute,可以添加一条新的路由规则记录作为现有路由的子路由。导航守卫
路由守卫用于路由跳转的一些验证
全局守卫:前置守卫:
beforeEach后置钩子:afterEach单个路由守卫:独享守卫:
beforeEnter组件内部守卫:
beforeRouteEnterbeforeRouteUpdatebeforeRouteLeave所有的路由守卫都是三个参数(to,from,next)
to: 要进入的目标路由(去哪儿)from: 要离开的路由(从哪来)next: 是否进行下一步(要不要继续)next()相当于next(true)放行,不写 相当于next(false)终止执行,next(path)跳转 例如:next("/login"),注意:后置钩子afterEach没有next参数
//main.js中设置全局路由前置守卫 import router from "./router/index.js"; // eslint-disable-next-line //忽略下行eslint校验 const login = false; router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { if (to.path !== "/user") next(); //如果不去/user路由,放行 else { if (login == true) { //如果登录,放行 next(); } else { //未登录跳转'/login'路由 next("/login"); } } });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17//路由独享的守卫(进入这个路由之前) { path: "/user", name: "user", component: User, // eslint-disable-next-line beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => { if (to.path !== "/user") next(); else { if (login == true) next(); else next("/login"); } }, },1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<!--组件内的守卫--> <div>用户信息</div> <script> const login = false; export default { data() { return { login: true, //不!能!获取组件实例 `this`,因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建 //可以通过next(vm => {// 通过 `vm` 访问组件实例}) //beforeRouteUpdate 和 beforeRouteLeave 来说,this 已经可用了,所以不支持传递回调 }; }, beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) { // eslint-disable-next-line if (login == true) next(); else next("/login"); }, }; </、script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20api
$router全局对象
push(path)
replace(path)
back()
go(-1/1...)
$route当前路由对象
params
query
path
name(路由表中定义)
其他
- Home 模板中使用的路由跳转标签
- 标签, 负责展示当前路由对应的组件内容
异步加载路由:component:( ) => import('../xxxx')
命名路由搭配 params,刷新页面参数会丢失
this.$router.push({ name: "news", params: { userId: 123 } });1查询参数搭配 query,刷新页面数据不会丢失
this.$router.push({ path: "/news", query: { userId: 123 } });1
# vue-route原理 (opens new window)
Vue.use(Router); //Router是插件,插件是函数或对象
// var a=function(){//第一个参数是vue构造函数
//console.log(vue);
// console.log("function")
// }
var a = {};
a.install = function (vue) {
//install方法的第一个参数是vue构造函数
console.log(vue);
console.log("install");
};
Vue.use(a); //use时会执行a中的代码,如果a有install属性,则执行install方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
//vueRoute.js
let Vue;
class VueRoute {
constructor(options) {
// console.log(options);
// this.current = "/";
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, "current", "/"); //将current实现响应式
console.log(this.current);
this.routes = options.routes; //用户定义路由表
this.modes = options.mode || "hash";
this.init(); //监听路由改变
this.push = () => {}; //...
}
init() {
if (this.modes === "hash") {
//第一次加载
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
this.current = location.hash.slice(1);
});
//地址栏改变时
window.addEventListener("hashchange", () => {
//通过hashchange监听
this.current = location.hash.slice(1);
});
} else {
//处理history
//利用了 HTML5 History Interface 中新增的 pushState() 和 replaceState() 方法结合window.popstate事件(监听浏览器前进后退)。
window.addEventListener('popstate',()=>{
})
}
}
}
VueRoute.install = (_vue) => {
Vue = _vue; //保存Vue
//创建全局组件
Vue.component("router-link", {
props: {
to: {
//使用组件需要传href
type: String,
require: true,
},
},
render(h) {
//创建html标签,router-link避免了重复渲
return h("a", { attrs: { href: "#" + this.to } }, this.$slots.default);
},
});
Vue.component("router-view", {
render(h) {
//变量为响应式的才执行
const { current, routes } = this.$router;
const com = routes.find((item) => item.path == current);
//console.log("com", com);
return h(com.component);
},
});
//全局混入,给vue原型添加router属性
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) {
//根实例
Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router; //给vue原型添加$router属性
}
},
});
};
export default VueRoute;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# 插件
对象形式
const obj = { install: function (app:any, options1:any,option2:any) { console.log("使用插件"); console.log('app',app); console.log(options1,option2); } } app.use(obj,'option1','option2')//执行install方法,1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8函数形式
const fun=function(app:any,opt1:any){ console.log(app); console.log(opt1); } app.use(fun,'option1')//执行函数1
2
3
4
5
6
# VueX (opens new window)
单向数据流
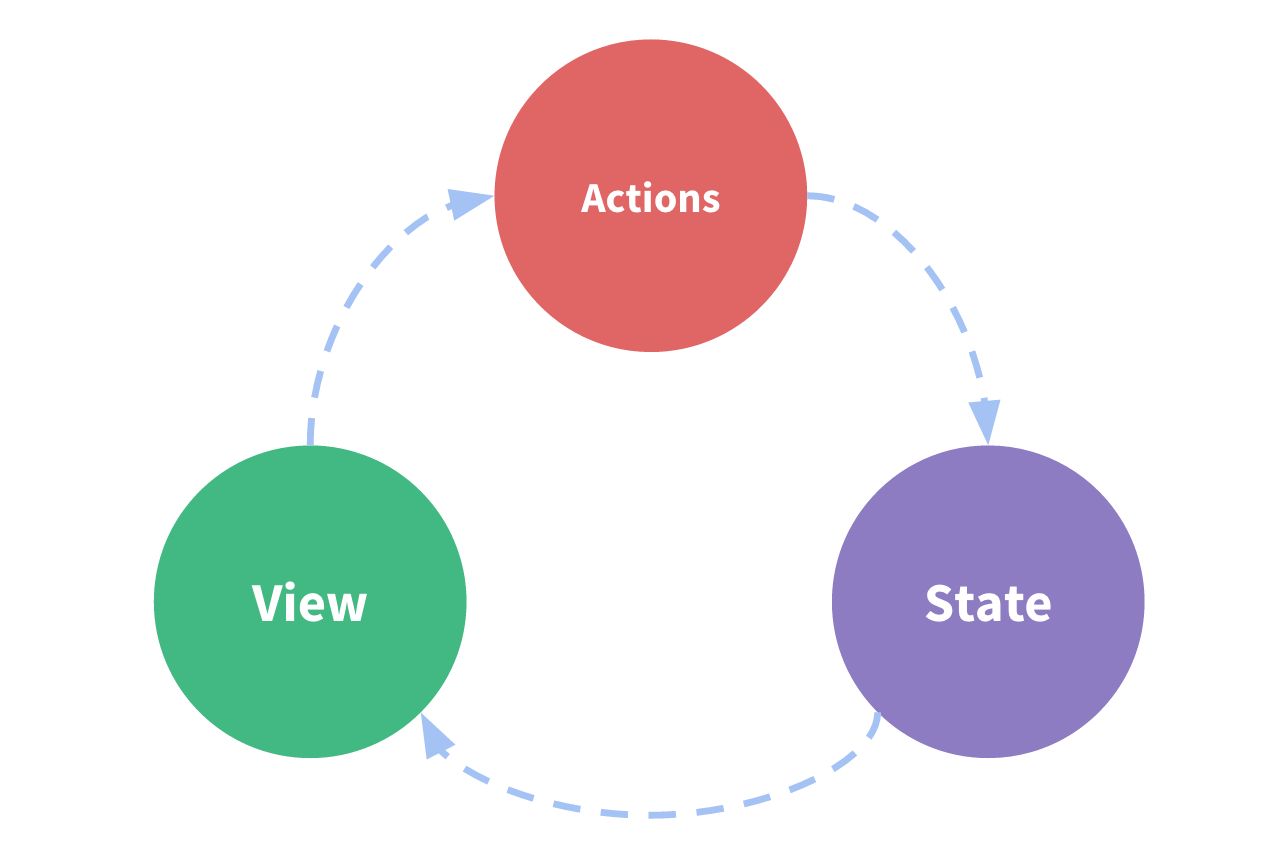
Vuex数据管理框架,VueX创建了一个全局唯一的仓库,用来存放全局的数据。//基本使用(vue add vuex) //创建store下的index.js文件 import Vue from "vue"; import Vuex from "vuex"; Vue.use(Vuex); //创建VueX对象 export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { //存放要管理的状态 count: 0, list: [ { tilie: "昔我往矣 (Wake up from the past)", time: "0:28" }, { tilie: "镜花水月 (The mirror)", time: "0:55" }, { tilie: "谁解其中味 (The secret)", time: "1:00" }, { tilie: "夜来幽梦 (Wake up)", time: "0:26" }, { tilie: "零落成泥 (Dust to dust)", time: "1:36" }, { tilie: "在水一方 (Where is she)", time: "1:38" }, ], }, mutations: { //这里是set方法 increment(state, payload) { state.count += payload; }, decrement(state, payload) { state.count -= payload; }, }, actions: { //异步操作 async({ commit }) { //Actions接受一个context对象参数,该参数具有和store实例相同的属性和方法 setTimeout(() => { commit("increase", 3); }, 1000); }, }, getters: { // 这里是get方法 newList(state) { state.list.push({ tilie: "送别 (Farewell by Ms.Chen)", time: "1:00", }); return state.list; }, }, });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49//需要在根实例中注册 store 选项,该 store 实例会注入到根组件下的所有子组件中,且子组件能通过 this.$store 访问到 import store from "./store/index"; new Vue({ store, render: (h) => h(App) }).$mount("#app"); //挂载1
2
3
4<!--子组件--> <template> <div> <!--添加对多个参数不能直接加',',否则第二个参数是undifined,应该封装成对象或数组--> <el-button @click="$store.commit('increment', 2)">加2</el-button> <el-button @click="$store.commit('decrement', 2)">减2</el-button> 总数:{{ $store.state.count }} </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Son", data() { return { //count:this.$store.state.count //这么写改变数据时页面不更新 }; }, }; </>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20核心内容
- state 存放状态
- mutations state 成员操作
commit(‘mutation’,paylod) - getters 加工 state 成员给外界
- actions 异步操作
dispatch(‘action’,paylod) - modules 模块化状态管理
增删 state 中的成员
//使用delete或者xx.xx = xx的形式去删或增,则Vue不能对数据进行实时响应。 Vue.set(state, "age", 15); //添加 Vue.delete(state, "age"); //删除1
2
3辅助函数
<!--子组件--> <el-button @click="increase(2)">加2</el-button> <!-- {{ $store.state.count }} --> {{count}} <el-button @click="decrease(2)">减2</el-button> <el-button @click="async">async</el-button> <el-table :data="newList" style="width: 30%" class="table"> <el-table-column type="index" label="编号" width="50"> </el-table-column> <el-table-column prop="tilie" label="曲目列表(中/英)" width="250"> </el-table-column> <el-table-column prop="time" label="时长"> </el-table-column> </el-table> <script> import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations } from "vuex"; export default { data() { return { // count: this.$store.state.count, //vuex中状态发生改变,并不会再次赋值给count,页面中数据也不会更新,直接在模板中使用state或使用mapState }; }, computed: { ...mapState(["list", "count"]), ...mapGetters(["newList"]), // ...mapState({renamecount:count,list})//可以重命名 }, methods: { ...mapMutations(["increase", "decrease"]), ...mapActions(["async"]), }, }; </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32规范目录结构
//如果把整个store都放在index.js中是不合理的,所以需要拆分。比较合适的目录格式如下: store:. │ actions.js │ getters.js │ index.js │ mutations.js │ mutations_type.js ##该项为存放mutaions方法常量的文件,按需要可加入 │ └─modules Astore.js //对应的内容存放在对应的文件中,和以前一样,在index.js中存放并导出store。state中的数据尽量放在index.js中。而modules中的Astore局部模块状态如果多的话也可以进行细分。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11Vue.observable
const state = Vue.observable({ count: 0 }) const Demo = { render(h) { return h('button', { on: { click: () => { state.count++ }} }, `count is: ${state.count}`) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<template> <div> {{ count }} <el-button @click="add">add</el-button> </div> </template> <script> import Vue from 'vue' const store = Vue.observable({ count: 1 }) export default { name: "test", computed: { count() {//模板中使用用computed return store.count } }, methods: { add() { store.count++ } } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# iframe
<!--父组件-->
<!--view.html需要在public目录下能够访问-->
<iframe
ref="iframe"
src="/view.html"
frameborder="no"
scrolling="no"
></iframe>
<button @click="send('君且西去,春事依然')">send to iframe</button>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
const iframe = this.$refs.iframe;
iframe.onload = () => {
//iframe加载完成才能获取iframe的window对象
this.iframeWin = iframe.contentWindow;
};
window.addEventListener("message", e=> {
//监听到子页面的传参
console.log(e.data);
});
},
methods:{
send(msg) {
//通过postMessage向iframe传参
this.iframeWin.postMessage(msg, "*");
},
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
<h1>iframe</h1>
<button onClick="send('秋鸿折单复难双,痴人痴怨恨迷狂。')">send to vue</button>
<script>
window.addEventListener('message', e => {
//console.log(e.data);
})
function send(msg){
window.parent.postMessage(msg,'*');
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
